In-situ testing of wall-to-diaphragm shear transferring
connections in an existing clay brick URM building
Earthquake Spectra, 34(1)
Scope and methodology
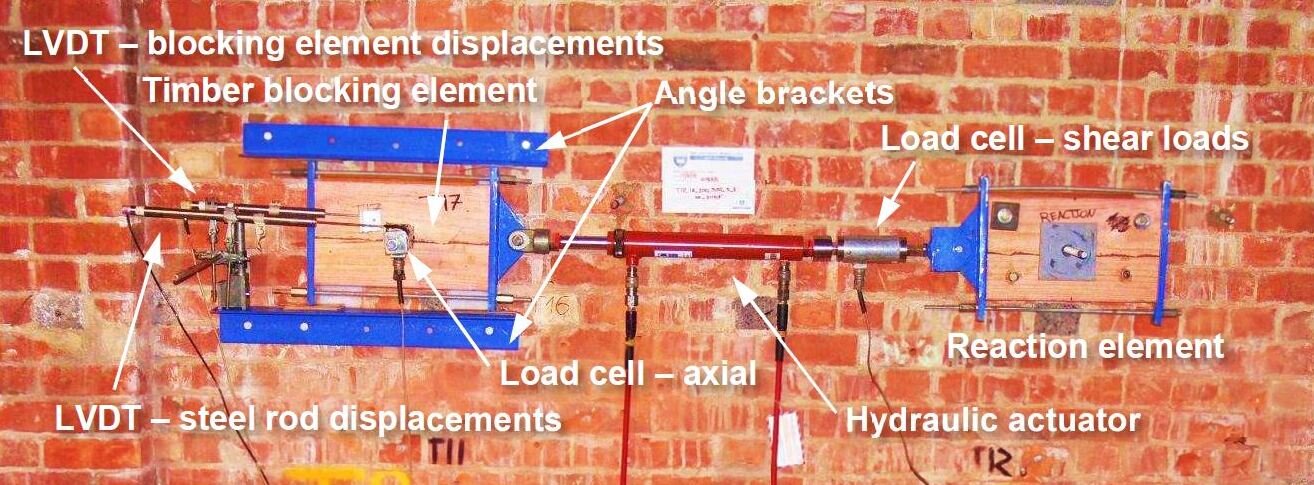
Field test campaign to study the effectiveness of adhesive anchors to transfer seismic shear action from the timber diaphragm to the resisting URM walls
22 cyclic shear tests of adhesive anchor rods varying: anchor rod diameter, embedment depth, timber blocking thickness, boundary conditions, washer size and axial pre-load of the anchor.
Direct tension pull-out tests also performed on selective anchors to define failure and residual anchor pull-out capacity.
An analytical formulation that was based on the Johansen Theory was used to evaluate the shear strength of the connection and the failure mode.
The preliminary stiffness characterisation of the wall-to-diaphragm shear transferring connection is also addressed.
FINDINGS
The variation of the axial force introduced by the nut tightening and the embedment depth of the anchor had no noticeable effect on the shear capacity of the anchors.
The thickness of the blocking element did not affect the shear behaviour of the specimen due to the s type steel washer allowing the formation of the second plastic hinge.
Local masonry crushing around the steel rod was observed, although without significant effects on the bearing capacity of the anchor.
A significant scatter in the experimentally derived stiffness results was obtained which made difficult to directly compare the effects produced by the variation of each parameter.
The analytical formulation proposed by Gattesco and Del Piccolo was modified to evaluate the shear capacity of adhesive anchors. It was shown that the proposed procedure leads to conservative results with an underestimation of the experimentally obtained shear capacities of approximately 20%.